Microsoft patch policies
If from Targets you can define when, how, and to whom updates are applied, from Microsoft patch policies you can define what gets updated; that is, you can manage the approval or denial of the installation of one or more updates from the Microsoft catalog on an organization's devices.
Create a new update policy
To define a new policy, you must click New at the top right of the table. A modal window will open with a form prompting you to assign a name to the new policy being created.
After clicking on Save, the name of the policy just created will appear in the table.
Microsoft update policies table
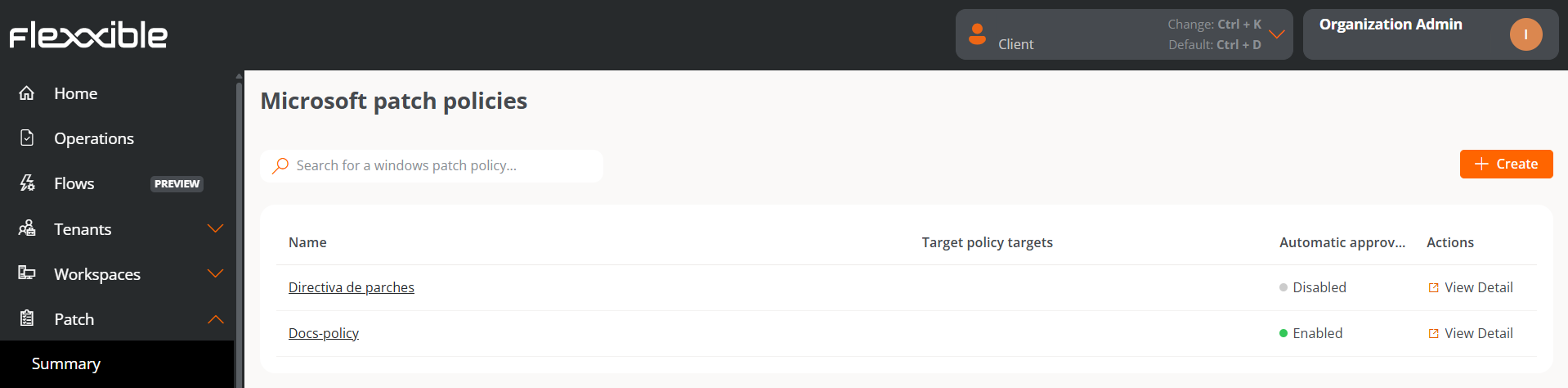
The table fields provide the following information:
- Name: name of the Microsoft update policy
- Target policy targets: targets configured with a Microsoft update policy.
- Automatic approvals: indicates whether the automatic approval settings are Enabled or Disabled.
- Actions: displays the link
View Details, which opens a window with the detailed view of the Microsoft Updates Policy.
Detail view
From this view, you can configure the Microsoft update policy in three areas:
Details
This tab displays precise information about the policy being consulted:
- Name: name of the Microsoft update policy being consulted.
- Targets: list of targets linked to the Microsoft update policy being consulted.
- Creation date: creation date of the Microsoft update policy being consulted.
- Created by: user who created the Microsoft update policy being consulted.
The Edit button opens a modal window allowing you to change the name of the policy and the Delete button discards it.
Microsoft patches
This tab displays a table listing the Microsoft updates available for the linked target. At the top, there are many filtering options to list available patches by Classifications, Products, Superseded, or Release Date. You can also search by character strings or by their status of Pending Approval, Approved, or Rejected.
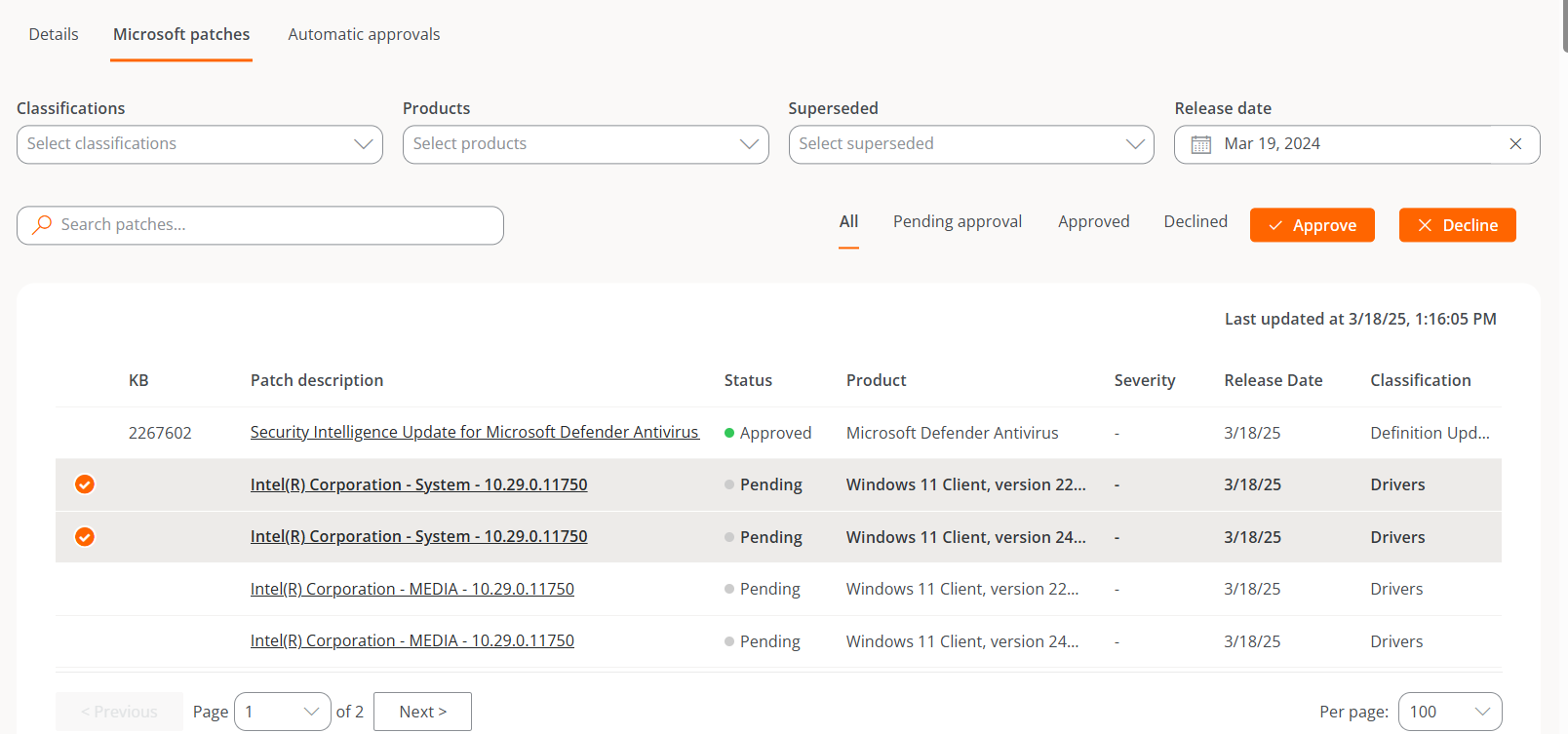
The user can select each available update one by one and indicate whether they want to approve or reject that patch.
If a user defines a Microsoft update policy, but does not manually or automatically approve or deny an update package, no patching activity (installation or uninstallation) will be generated on the devices.
Automatic Approvals
Automatic approval rules can be configured for patching, even more than one within the same update policy.
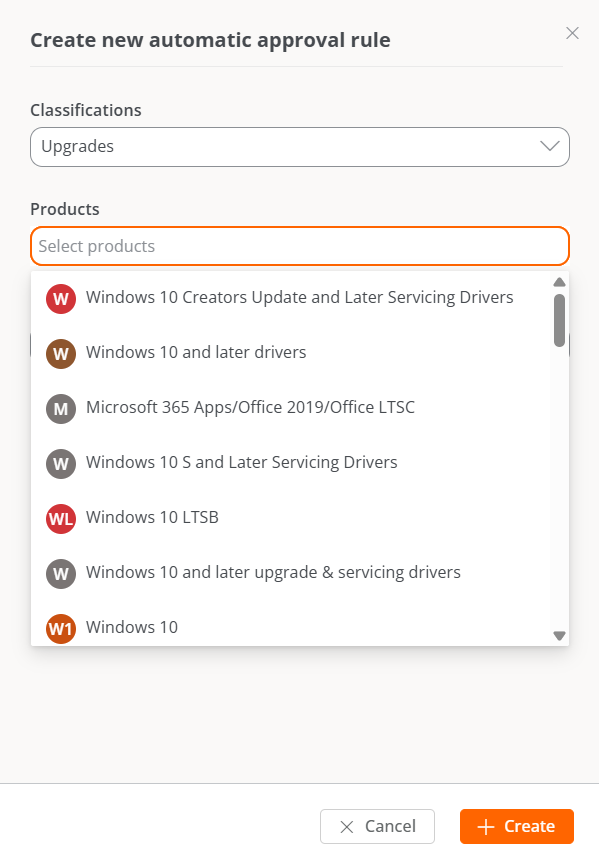
To create a new rule, click on New. Next, a modal window will open asking to define the following information:
- Classifications: distinguishes patches according to their category (Security updates, Feature packs, Updates, Critical updates, Drivers, Upgrades and Definition updates).
- Products: allows selecting the Microsoft product the update applies to.
- Days after release: allows specifying how many days after the patch release date it will be automatically approved.
Flexxible recommends setting up automatic patch approval rules whenever a new update policy is created, and not applying the new policy to the desired target until the updates intended as a starting point are approved. In this way, you can start from a scenario where all previous updates are approved for user devices.